Prostate cancer is a common type of cancer in males, but it is highly treatable in the early stages. It begins in the prostate gland, which sits between the penis and the bladder.
The prostate is a small walnut-shaped gland in males that produces the seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm.
Many prostate cancers grow slowly and are confined to the prostate gland, where they may not cause serious harm. However, while some types of prostate cancer grow slowly and may need minimal or even no treatment, other types are aggressive and can spread quickly. (1)
Prostate cancer that’s detected early — when it’s still confined to the prostate gland — has the best chance of successful treatment.
Signs and symptoms
There are often no symptoms during the early stages of prostate cancer, but screening can detect changes that may indicate cancer. Screening involves a test that measures levels of PSA in the blood. High levels suggest that cancer may be present.
Males who do experience symptoms may notice:(2)
- Difficulty starting urination.
- Weak or interrupted flow of urine.
- Urinating often, especially at night.
- Trouble emptying the bladder.
- Pain or burning during urination.
- Blood in the urine or semen.
- Pain in the back, hips, or pelvis that doesn’t go away.
- Painful ejaculation.
What Is Screening for Prostate Cancer? (3)
Cancer screening means looking for cancer before it causes symptoms. The goal of screening for prostate cancer is to find cancers that may be at high risk for spreading if not treated, and to find them early before they spread.
If you are thinking about being screened, learn about the possible benefits and harms of screening, diagnosis, and treatment, and talk to your doctor about your risk factors.
There is no standard test to screen for prostate cancer. Two tests that are commonly used to screen for prostate cancer are described below.
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Test(3)
A blood test called a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test measures the level of PSA in the blood. PSA is a substance made by the prostate. The levels of PSA in the blood can be higher in men who have prostate cancer. The PSA level may also be elevated in other prostate conditions.
As a rule, the higher the PSA level in the blood, the more likely a prostate problem is present. But many factors, such as age and race, can affect PSA levels. Some prostate glands make more PSA than others.
PSA levels also can be affected by:
- Certain medical procedures.
- Certain medications.
- An enlarged prostate.
- A prostate infection.
Because many factors can affect PSA levels, your doctor is the best person to interpret your PSA test results. If the PSA test is abnormal, your doctor may recommend a biopsy to find out if you have prostate cancer.
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Test(3)
Digital rectal examination (DRE) is when a health care provider inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into a man’s rectum to feel the prostate for anything abnormal, such as cancer. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force does not recommend DRE as a screening test because of a lack of evidence on the benefits.
Causes
Researchers are unsure of the exact cause of prostate cancer. It develops when specific changes occur, usually in glandular cells. When prostate gland cells appear abnormal, a doctor may refer to these changes as prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN). Nearly 50% of all males over the age of 50 years have a PIN.(4)
At first, the changes will be slow, and the cells will not be cancerous. However, they can become cancerous with time. Cancer cells can be high or low grade. High-grade cells are more likely to grow and spread, while low-grade cells are not likely to grow and are not a cause for concern. (4)
Risk factors (1)
- Age: The risk of prostate cancer increases after the age of 50, but it is rare before 45.
- Race or ethnicity: The condition is more common in Black people than white people. Asian and Hispanic people have a lower risk than Black or white people.
- Family history: A person with a close relative who has a history of prostate cancer has a higher chance of developing it themselves.
- Genetic factors: Inherited features, including changes to the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, may increase the risk. Mutations in these genes also increase the chance of breast cancer. Men born with Lynch syndrome also have a higher risk of prostate and other cancers.
- Diet: Some evidence suggests that high-fat diets may increase the risk of prostate cancer.
Other factors that may influence prostate cancer risk include:(5)
- obesity
- smoking
- alcohol consumption
- exposure to chemicals, such as the herbicide Agent Orange
- inflammation of the prostate
- sexually transmitted infections
- vasectomy surgery
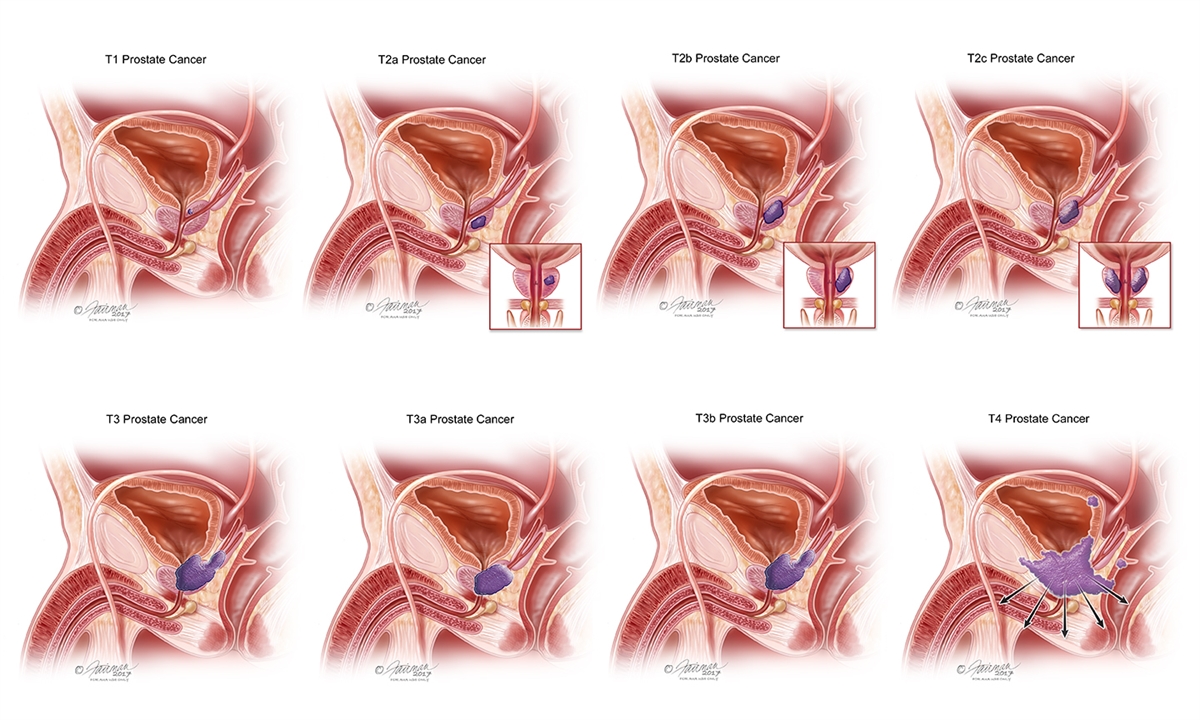
Stages
Staging typically describes how much cancer is present in the body and how serious the cancer is. Knowing the stage of prostate cancer can help a person understand what to expect and will inform decisions about treatment.
Cancer staging is complex and accounts for many different factors. Usually, the lower the number, the less cancer has spread. Stages may include:(5)
- Stage I: Cancer is only present in the prostate gland.
- Stage II: Cancer has not yet spread from the prostate, but a person will have a higher PSA level.
- Stage III: Cancer may have spread to nearby tissues.
- Stage IV: Cancer may have spread to distant parts of the body.
How Is Prostate Cancer Treated? (6)
Different types of treatment are available for prostate cancer. You and your doctor will decide which treatment is right for you. Some common treatments are:
- Expectant management. If your doctor thinks your prostate cancer is unlikely to grow quickly, he or she may recommend that you don’t treat cancer right away. Instead, you can choose to wait and see if you get symptoms in one of two ways:
- Active surveillance. Closely monitoring prostate cancer by performing prostate specific antigen (PSA) tests and prostate biopsies regularly, and treating cancer only if it grows or causes symptoms.
- Watchful waiting. No tests are done. Your doctor treats any symptoms when they develop. This is usually recommended for men who are expected to live for 10 more years or less.
- Surgery. A prostatectomy is an operation where doctors remove the prostate. Radical prostatectomy removes the prostate as well as the surrounding tissue.
- Radiation therapy. Using high-energy rays (similar to X-rays) to kill cancer. There are two types of radiation therapy—
- External radiation therapy. A machine outside the body directs radiation at the cancer cells.
- Internal radiation therapy (brachytherapy). Radioactive seeds or pellets are surgically placed into or near cancer to destroy the cancer cells.
Other therapies used in the treatment of prostate cancer that is still under investigation include—
- Cryotherapy. Placing a special probe inside or near the prostate cancer to freeze and kill the cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy. Using special drugs to shrink or kill cancer. The drugs can be pills you take or medicines given through your veins, or, sometimes, both.
- Biological therapy. Works with your body’s immune system to help it fight cancer or to control side effects from other cancer treatments. Side effects are how your body reacts to drugs or other treatments.
- High-intensity focused ultrasound. This therapy directs high-energy sound waves (ultrasound) at cancer to kill cancer cells.
- Hormone therapy. Blocks cancer cells from getting the hormones they need to grow.
Can Prostate Cancer Be Prevented? (7)
There is no sure way to prevent prostate cancer. Many risk factors such as age, race, and family history can’t be controlled. But there are some things you can do that might lower your risk of prostate cancer.
- Get to and stay at a healthy weight.
- Keep physically active.
- Follow a healthy eating pattern, which includes a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables and whole grains, and avoid or limit red and processed meats, sugar-sweetened beverages, and highly processed foods.
Vitamin E and selenium: Some early studies suggested that taking vitamin E or selenium supplements might lower prostate cancer risk.
Soy and isoflavones: Some early research has suggested possible benefits from soy proteins (called isoflavones) in lowering prostate cancer risk.
Taking any supplements can have both risks and benefits. Before starting vitamins or other supplements, talk with your doctor.
References:
- Rock CL, Thomson C, Gansler T, Gapstur SM, McCullough ML, Patel A v., et al. American Cancer Society guideline for diet and physical activity for cancer prevention. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020 Jul;70(4):245–71.
- What Are the Symptoms of Prostate Cancer? | CDC [Internet]. [cited 2022 Sep 4]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/prostate/basic_info/symptoms.htm
- What Is Screening for Prostate Cancer? | CDC [Internet]. [cited 2022 Sep 4]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/prostate/basic_info/screening.htm
- Prostate cancer: Symptoms, treatment, and causes [Internet]. [cited 2022 Sep 4]. Available from: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/150086#causes
- Prostate cancer: Symptoms, treatment, and causes [Internet]. [cited 2022 Sep 4]. Available from: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/150086#risk-factors
- How Is Prostate Cancer Treated? | CDC [Internet]. [cited 2022 Sep 4]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/prostate/basic_info/treatment.htm
- Rock CL, Thomson C, Gansler T, Gapstur SM, McCullough ML, Patel A v., et al. American Cancer Society guideline for diet and physical activity for cancer prevention. CA Cancer J Clin [Internet]. 2020 Jul [cited 2022 Sep 4];70(4):245–71. Available from: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/prostate-cancer/causes-risks-prevention/prevention.html





Write a comment
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required